How To Find The Ph Of A Solution
Abstract: pH is a unit of measurement of measurement often used in fundamental chemical science concepts. "How to Calculate pH" explains it'southward categories the scientific mathematics and role pH has in our lives.
Terms to Be Familiar With:
- pH
- pOH
- Hydrogen ion
- Hydroxide ion
- Acid
- Base
What is pH?
The term "pH" is an abbreviation for the "potential of hydrogen." pH is a unit of measurement which represents the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. This unit was introduced past biochemist Søren Peter Lauritz Sørensen in 1909. It was an easy mode to represent the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution during titrations. When an acid or base is added to h2o, that chemical compound dissociates into ions. For acids 1 of those ions is a hydrogen ion (H+) and for bases 1 of the ions is a hydroxide ion (OH–). This description of acids and bases is known as the Arrhenius Theory. The concentration of hydrogen ions are often described by the pH scale as a numeric value.
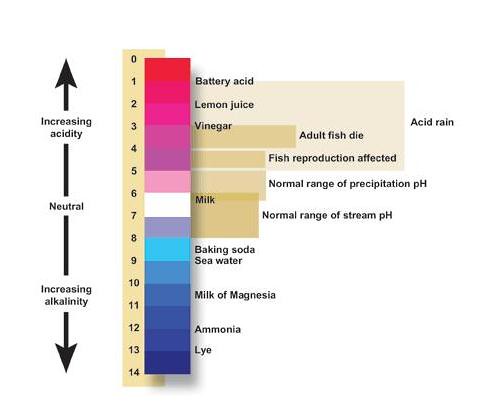
The pH Scale: Acidic, Neutral, and Basic
The pH calibration describes the acidity of the solution: acidic, neutral, or basic A solution with a pH less than 7 is an acid, exactly 7 is a neutral solution, and above vii is a base. Bases accept less hydrogen ions but more hydroxide ions, represented past the pOH or "potential of hydroxide ions."
Table i. The pH Scale
| Acidic | Neutral | Bones |
| Less than 7 | 7 | Greater than 7 |
Many other scientists studied the proprieties of acids and bases from the ideas of Sorensen and Arrhenius and came upwards with their own definitions. A notable theory is known as the Bronsted-Lowry Theory. The Bronsted-Lowry Theory is a concept involving acid and bases which suggest that acids human action every bit proton donors. Since neutral hydrogen atoms are usually made of one proton and one electron, a positive hydrogen ion is often referred to as a proton. These protons carry a positive charge and are given away to the bases. Bases, with that logic, are proton acceptors. Bases, carrying lone pairs of electrons, concenter positive hydrogen ions (protons).
In the lab, pH can be determined past a pH indicator such as pH paper. pH newspaper usually contains a weak acid or a weak base which volition respond by changing color at a specific pH. This method is used ofttimes as a cheap, quick way to decide pH rather than using pH meters which demand frequent calibration and maintenance. Keep in listen that very depression or very high pH value solutions can be very caustic and should be handled with care.
Practice Problems
Determine if the following solution is acidic, neutral, or basic.
- pH = ane.00
- pH = ten.00
- pH = half-dozen.99
- pH = 7.02
- pH = eight.00
- pH = xiii.00
- pH = ii.00
Answers:
- Acidic
- Basic
- Neutral
- Neutral
- Basic
- Basic
- Acidic
Concentrations of H+ and OH–
Concentration is the amount of solute in respect to the amount of full solution. A loftier amount of solute equals a high concentration, where a lower amount of solute would equal a low overall concentration.
When an acrid or a base is placed into a solvent, that chemical compound will dissociate into ions. The concentration of H+ (hydrogen ions) in the solution will determine the acerbity or basicity of the solution. A high concentration of H+ will signify an acidic solution and a low concentration of H+ volition signify a bones solution.
In hydrochloric acid for example (a mutual acid that is an aqueous solution of HCl), HCl molecules have dissociated into two kinds of ions, H+ and Cl–. This dissociation produces a high H+ concentration, which is a property of an acidic solution.
The same can be seen in basic solutions where there is a low H+ concentration, due to the high
OH– (hydroxide ion). For example, when NaOH (sodium hydroxide, a mutual base), is placed in h2o, it dissociates into two kinds of ions, Na+ and OH–. The high OH– concentration, which corresponds to a low H+ concentration, is a belongings of basic solution.
Table 2. Relationship Between pH and pOH
| Concentration of H+ | Concentration of -OH | Case(s) | |
| Acrid | High | Low | HCl, HCOOH, HNO3 |
| Base of operations | Depression | High | NaOH, MgO, CaCO3 |
| Neutral | Equal to OH– | Equal to H+ | H2o |
The conclusion of pH and pOH will exist calculated by using the concentration of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions respectively. pH and pOH also have a human relationship so that if you practise not take enough information to decide ane, you can utilize the concentration of the other. This will be done through Sorensen's equation for computing pH.
How to Calculate pH
Note: Delight use a scientific figurer.
pH is determined by the concentration of H+, which is frequently summarized every bit [H+]. This can be calculated past the following equation:
pH=-log { \left[ { H }^{ + } \right] } or pH=log { \left( \dfrac { ane }{ \left[ { H }^{ + } \right] } \right) }
Conversely, the hydrogen concentration tin can exist found by a given pH. The [H+] can exist calculated past the following equation.
\left[ { H }^{ + } \correct] ={ 10 }^{ -pH }
The determination of the concentration of hydrogen ions and pH will later be used to show the human relationship between pH and pOH.
Key Equations:
pH=-log { \left[ { H }^{ + } \correct] } or pH=log { \left( \dfrac { 1 }{ \left[ { H }^{ + } \correct] } \right) }
\left[ { H }^{ + } \right] ={ ten }^{ -pH }
Example 1: Calculate the pH of a 0.200 M HCl solution.
HCl solutions are potent acids, so we tin already await a pH less than 7. Using the 0.200 M HCl as the [H+] (concentration of hydrogen ions) the solution is as follows:
pH=-log { \left[ { H }^{ + } \right] } = log(0.200) =0.70
A 0.70 pH indicates a very acidic solution.
Instance 2: Summate the pH of a 0.100 M nitric acid solution.
Nitric acid has a chemic formula of HNOthree. HNOthree is another stiff acid, so the pH of this solution will too be less than 7. Using the 0.100 Thousand nitric acid as the [H+] (concentration of hydrogen ions) the solution is as follows:
pH=-log { \left[ { H }^{ + } \right] } = log (0.100) = 1.00
A 1.00 pH indicates a very acidic solution.
In examples 1 and two nosotros are able to use the concentration of the acid as the concentration of the H+ ion considering every acid molecule dissociates, thereby releasing an H+ ion. These types of acids are referred to as "strong acids". For "weak acids", most of the acid molecules practise non dissociate, so nosotros would have to use more complex methods to calculate pH for solutions of weak acids. We'll stick to strong acids and bases in this article, and explore weak acids and base in another commodity.
Case 3. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution that has a pH of 4.30?
This example provides the reverse information. Here, we are given the concentration of H+ in a solution and are asked to decide the pH.
four.xxx = -log { \left[ { H }^{ + } \correct] }
-4.30 = log { \left[ { H }^{ + } \correct] }
\left[ { H }^{ + } \right] ={ 10 }^{ -4.30 }M=v.01x{ 10 }^{ -5 }Thou
How to Calculate pOH
pOH is determined past the concentration of OH–, [OH–]. This can be calculated by the post-obit equation:
pOH=-log { \left[ { OH }^{ - } \correct] } or pOH=log { \left( \dfrac { 1 }{ \left[ { OH }^{ - } \right] } \correct) }
Conversely, the hydroxide concentration can be found past a given pOH. The [OH–] can exist calculated by the following equation.
\left[ { OH }^{ - } \correct] ={ 10 }^{ -pOH }
pOH is a different mode of describing acerbity and basicity, so be conscientious not to mix information technology upwards with pH. The descriptions for solutions based on the pOH calibration are given in Table ii.
Table 3. The pOH Scale
| Bones | Neutral | Acidic |
| Less than 7 | 7 | Greater than seven |
The determination of the concentration of hydroxide ions and pOH will be later used to prove the relationship between pH and pOH.
Key Equations:
pOH=-log { \left[ { OH }^{ - } \right] } or pOH=log { \left( \dfrac { 1 }{ \left[ { OH }^{ - } \right] } \right) }
\left[ { OH }^{ - } \correct] ={ x }^{ -pOH }
Example one: Calculate the pOH of a 1.xx M NaOH solution.
This is calculated similarly to the conclusion of pH. Instead of determining the pH, we will be determining the pOH with employ of -log[OH–]. NaOH volition dissociate completely in solution, so we can use the concentration of NaOH equally the concentration of OH–.
pOH=-log { \left[ { OH }^{ - } \right] } = log(ane.20) = -0.08
A -0.08 pOH indicates a very basic solution.
Case 2: Calculate the pOH of a solution with a hydroxide concentration of 5.23 x ten-5 Thou.
pOH=-log { \left[ { OH }^{ - } \right] } = log(five.23 x 10^{-5}) = 4.20
Example iii. What is the hydroxide concentration of a solution that has a pOH of 11.30?
This example provides the opposite data. Here, nosotros are given the concentration of OH– in a solution and are asked to determine the pOH. This is washed similarly to the determination of hydrogen concentration from a pH.
11.30 = -log { \left[ { OH }^{ - } \correct] }
– xi.xxx = log { \left[ { OH }^{ - } \right] }
{ \left[ { OH }^{ - } \correct] }={ ten }^{ -11.30 }One thousand=5.01x{ 10 }^{ -12 }
Summate the Relationship Betwixt pH and pOH
In the department "Concentrations of H+ and OH–" we discussed that the loftier concentration of hydroxide ions left little room for hydrogen ions and vice versa. The relationship of pH and pOH is that both values will equal 14.00. This tin exist represented in the following equation:
pH + pOH = xiv.00
You tin can check your work by adding the pH and pOH to ensure that the total equals 14.00. This likewise is an excellent representation of the concept of pH neutrality, where equal concentrations of [H+] and [OH–] result in having both pH and pOH every bit 7.
pH+pOH=14.00
pH=fourteen-pOH
pH=14-pH
Example 1: What is the pH of a solution that has a pOH of 12.40?
Go along in heed that the relationship of pH and pOH equals xiv.
pH+pOH = 14.00
pOH = 12.xl
pH= unknown
pH +12.40 = 14.00
pH =1.60
Cheque Your Work: one.60 + 12.40 = xiv.00
Example 2: What is the pOH of a solution that has a [H+] of 0.100 M HCl?
Commencement, determine the pH and employ that value with the relationship of pH and pOH.
pH+pOH = 14.00
pH = -log[0.1000] = 1.00
i.00 + pOH = 14.00
pOH = thirteen.00
Bank check Your Work: i.00 + xiii.00 = 14.00
Example 3: What is the pOH of a solution that has a pH of iii.xl?
Go along in mind that the relationship of pH and pOH equals 14.00.
pH+pOH = xiv.00
pH = 3.40
pOH = unknown
pOH+iii.twoscore = 14.00
pOH=10.60 = pH 10.60
Check Your Work: 10.lx + three.40 = 14.00
The Importance of pH
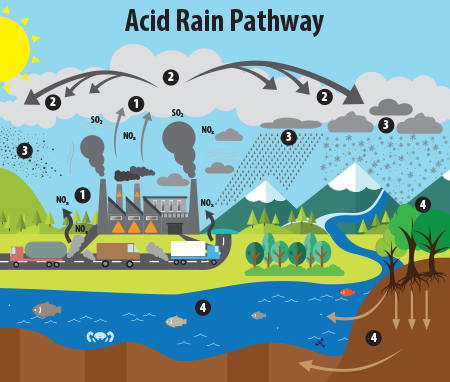
pH is all around us. It is important that vital solutions such as h2o, stomach acid, and blood maintain a consistent pH. Water, with a neutral pH of around 7, determines the solubility of many compounds. Without the appropriate pH of water, many chemical reactions would not occur. This can besides exist seen through naturally occurring phenomena such every bit acid pelting. Highly acidic atmospheric precipitation can cause erosion and other chancy environmental outcomes.
pH plays an important role in the solutions in the human trunk. Specific pH values are vital to the roles of solutions such every bit saliva, stomach acid, and blood. The production of saliva in the mouth is known equally the first step of digestion. Throughout the digestive tract, food must be broken down by acidic solutions. It is important that the pH of saliva should exist between 6.five-vii.5, slightly acidic, to begin this process. Later on, breadbasket acrid functions in the digestive system as well. It is important that breadbasket acrid has a very acidic pH, ranging from about 1.5 to 3.5, due to the secretion of HCl and the high concentration of hydrogen ions. This strongly acidic environment kicks digestion into loftier gear and begins to break downwards food particles in preparation for the excretion process.
Healthy blood has a pH of seven.4. Hundreds of reactions occur in the bloodstream, such as enzymes, which crave a specific pH. Blood with a higher or lower pH can result in negative symptoms. Acidosis is a symptom of a condition in which the pH value of claret is too low and alkalosis indicates blood with a pH value which is besides high.
Humans aren't the but organisms that rely on appropriate pH levels. Some species only thrive in alkaline (bones) environments and would not exist able to survive in neutral or acidic environments. Entire ecosystems revolve around pH.
Questions for Discussion
- Why is it of import that oceans keep a specific pH?
- Proper noun some mutual household items with an basic pH.
- What is the pH of vinegar? Why?
- If a patient suffers from acidosis, what are they suffering from?
- How does pH play a function in the blood?
More with pH: Acid-Base Equilibrium, Titrations, Buffers, pKa, Equilibrium Constant, Neutralization, Conjugate Acids, Conjugate Base.
Looking for Chemistry practice?
Check out our other articles on Chemistry.
You can also notice thousands of practice questions on Albert.io. Albert.io lets you customize your learning experience to target practice where you need the almost help. We'll give you challenging practice questions to assist you achieve mastery in Chemistry.
Start practicing hither .
Are you a teacher or administrator interested in boosting Chemistry student outcomes?
Learn more about our schoolhouse licenses hither.
Source: https://www.albert.io/blog/how-to-calculate-ph-in-chemistry/
Posted by: coatesperis1986.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find The Ph Of A Solution"
Post a Comment